Read digital input, digital output value, analog input, and count value
The sampling data of continuous input (sampling) is also read with this VI
|
|
|
|
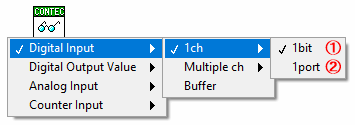
Select when digital input 1 bit *1
Select when digital input 1 port (8bit) together *1
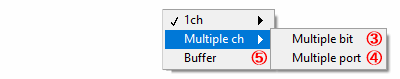
③ Digital input (Multiple bit)
Select when digital input multiple bits together
④ Digital input (Multiple ports)
Select when digital input multiple ports together
Select to acquire sampling data of digital input *2
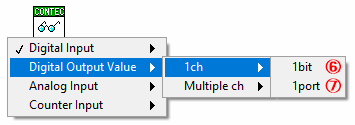
Select when acquiring 1 bit digital output value
⑦ Digital Output Value (1port)
Select when acquiring 1 port digital output value
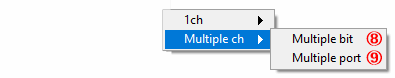
⑧ Digital Output Value (Multiple bit)
Select when acquiring the digital output value of multiple bits collectively
⑨ Digital Output Value (Multiple port)
Select when acquiring the digital output value of multiple ports collectively
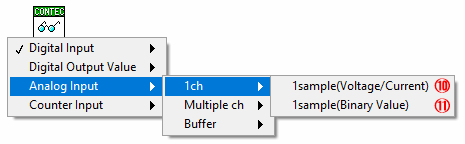
⑩ Analog input (1ch: Voltage/Current)
Select when analog input from 1 channel for one time and get the voltage/current value
⑪ Analog input (1ch: Binary Value)
Select when analog input from 1 channel for one time and get the binary value
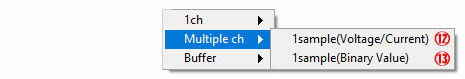
⑫ Analog input (Multiple ch: Voltage/Current)
Select when analog input from multiple channels for one time and get the voltage/current value
⑬ Analog input (Multiple ch: Binary Value)
Select when analog input from multiple channels for one time and get the binary value
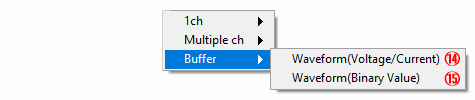
⑭ Analog input (Buffer: Voltage/Current)
Select when get the voltage/current data of continuous analog input
⑮ Analog input (Buffer: Binary Value)
Select when get the binary data of continuous analog input
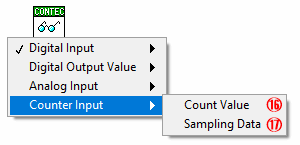
Select to read the count value of the counter input *3
Select to acquire sampling data of counter input *4
*1 Also supports digital input of analog devices and counter devices
*2 It can only be used with the following bus master type digital devices
PIO-32DM(PCI), DIO-32DM2-PE, DIO-32DM3-PE
*3 Also supports counter input of digital devices
*4 It can only be used with the following counter devices with sampling
function
CNT32-8M(PCI), CNT32-4MT(LPCI)
CNT-3208M-PE, CNT-3204MT-LPE
CNT-3204IN-USB
For example, if the resolution of analog device is 12 bit, as the operation of the hardware, the voltage width of set range will be divided into 4096 (12Bit), the divided value is called binary value. Example: If the range is ±10V The binary value 0 corresponds to -10V, the binary value 2047 corresponds to about 0V, the binary value 4095 corresponds to +10V, and the voltage difference between the binary values 0 and 1 is about 0.004883V (4.883mV) The voltage value is easy to understand intuitively, but the binary value is directly used by hardware, and there is no calculation error when voltage conversion. So the value is more accurate. And, current is the same.
|