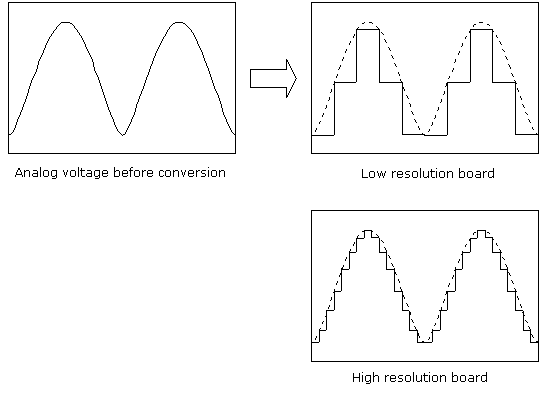
Resolution refers to the number of bits used to represent an analog
signal on an analog input device.
The higher the resolution which could make the voltage range to be divided
finely, could convert the analog value more accurate to the digital value.
Devices with 12-bit resolution divide the range width by 4096.
If the range of the device is 0 to 10V, the minimum unit of converted voltage
will be 10 ÷ 4096 = 2.44 mV.
If the range of the device is 0 to 20mA, the minimum
unit of converted current will be 20 ÷ 4096 = 4.88 mA.
Devices with 16-bit resolution divide the range
width by 65536.
If the range of the device is 0 to 10V, the minimum
unit of converted voltage will be 10 ÷ 65536 = 0.153 mV.
If the range of the device is 0 to 20mA, the minimum
unit of converted current will be 20 ÷ 65536 = 0.305 mA.
